This is AWESOME! I FULLY AGREE! Although, this should be a nation wide law and extended to the legal working age of 15 ½, 16 and or 18 and under; Not 14! I myself grew up in a time before the internet and if you wished to use the webs in the 90’s, you sat at a desk if you were lucky to have such access. Not everyone had a computer, or internet access/aka…. AOL. Our Social Media Platforms are just riddled with B.S., Fake Information, News and other crap! Anyway, I’m not saying the internet is a bad thing, it’s does a tremendous amount of good! In which KIDS SHOULD have access to; But the majority of social media SHOULD BE for 18 plus only!
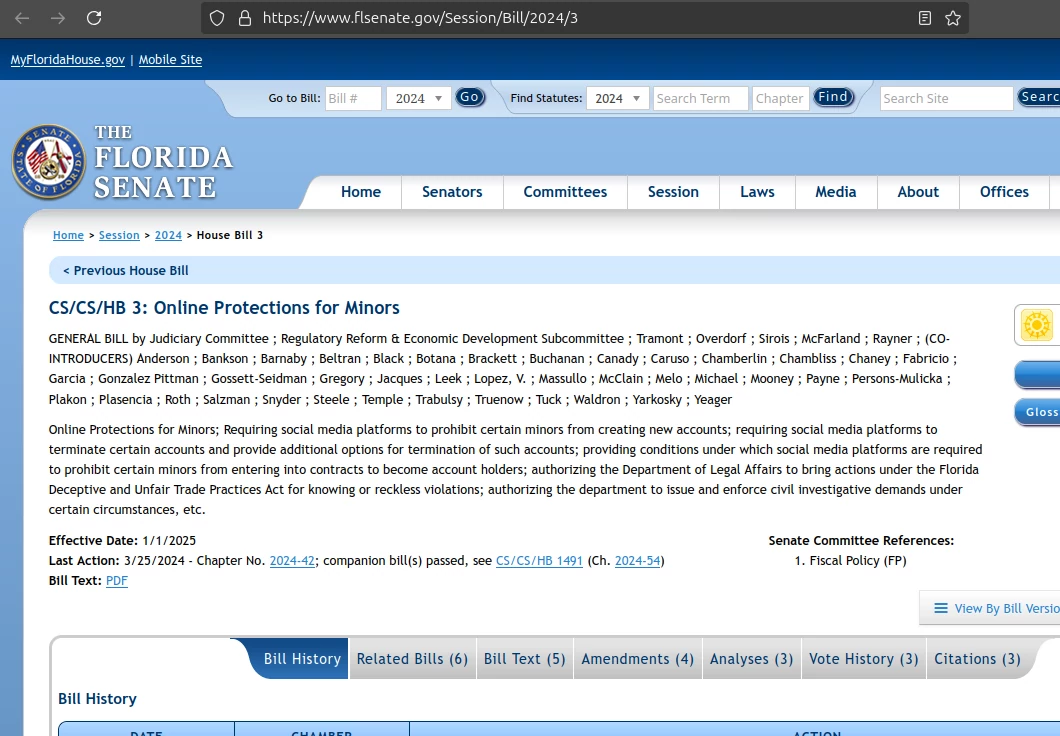
House Bill 3, the “Online Protections for Minors,” https://www.flsenate.gov/Session/Bill/2024/3
A new Florida law, effective Wednesday, prohibits children under the age of 14 from using social media platforms. The legislation mandates that social media companies delete accounts belonging to users under 14 within 90 days or face fines of up to $50,000 for each violation. Minors aged 14 and 15 can still access social media but only with parental consent.
House Bill 3, titled “Online Protections for Minors,” received bipartisan support and was signed into law last year by Governor Ron DeSantis. However, enforcement has been delayed until late February, pending a judge’s decision on a motion for a preliminary injunction filed by opponents. The delay leaves the law’s future uncertain, as social media companies prepare for potential legal and operational challenges.
“It’s very possible they will be enforced, though there will be several interesting variables to watch as the process unfolds,” said Dr. Cliff Lampe, professor of information and associate dean of academic affairs at the University of Michigan. Enforcement complexities arise partly because the number of Florida minors currently on social media is unknown. Lampe added, “In terms of enforcement, the easiest thing to do is to put pressure on the Apple and Android platforms to ‘de-platform’ the application, and then combine that with IP blocks so that enforcement becomes almost automatic.”
Supporters of the law argue it is necessary to safeguard children from the risks of online harassment and bullying. Opponents counter that the ban is overly restrictive and raises questions about practicality. “We all want to protect our children, keep them safe, and avoid harassment, bullying, and the other darkness that permeates social media these days. But, is banning minors from social media platforms realistic?” asked Susan Schreiner, a technology analyst at C4 Trends. She continued, “Until now, safety has fallen on the parents of children—but in an online world, what’s the shared responsibility of the platforms, or do they not care?”
Critics point out that the digital nature of social media complicates enforcement compared to physical goods like cigarettes, which are easier to regulate. Schreiner highlighted that lawmakers have adopted legislation to address the inaction of tech companies, stating, “Just consider the recent defeat of the Kids Online Safety Act in the U.S. which had broad bipartisan support.”
While the law is now in effect, Attorney General Ashley Moody has agreed not to enforce it during ongoing litigation. Schreiner explained, “In October, parties filed a lawsuit against the Florida law saying that some states have ‘taken it upon themselves to restrict minors’ access to constitutionally protected speech.'”
If upheld, the Florida law could set a precedent for other states and reshape how social media platforms operate. The timing of the law coincides with broader national discussions, including a potential nationwide ban on TikTok. “The U.S. has not banned a very popular application before, though there is a history of shutting down individual smaller sites for a variety of reasons,” Lampe noted. He added, “If the concern is national security, it seems there are more effective solutions than total blocks—but people often look for the largest visibility in a solution.”
The future of this legislation and its impact on social media regulation remain to be seen. For now, the law’s challenges underscore the complexities of balancing child safety with constitutional rights in the digital age.
Author: Ryan Bridglal, 01-02-2026